You’ve decided you want to invest in real estate. Or maybe you’re interested in selling your property.
But how much is that property worth?
In commercial real estate, there are three main appraisal methods: the income approach, the cost approach, and the comparison approach. Of these valuation methods, the income approach is most commonly used to determine the value of income-producing properties, such as commercial and multi-family buildings.
In this blog post, we’ll go through how the income approach works, a few examples, some considerations, and a comparison to other property appraisal methods.
What Is The Income Approach And What Does It Involve?
First, let’s dive into what the income approach is and what factors are used in calculating value.
The income approach (also known as the income capitalization approach) is a method for appraising real estate investments. It is performed by dividing the net operating income by the capitalization rate. The income approach is the primary way to value commercial real estate investments.
The income approach is akin to valuing a business using its income multiple. The capitalization rate is the inverse of the multiple. For instance, a 5% cap rate is the same as a 20x multiple.
To calculate the income approach, you need two pieces of information:
Net Operating Income (NOI):
This is the income a property generates, minus any operating expenses. Operating expenses include items such as property management, property taxes, insurance, utilities, and repairs and maintenance.
Net operating income doesn’t include any costs of debt service or capital expenditures. By removing these from the expenses, the value can be determined strictly by the operation of the business.
Real estate investors should be sure to factor vacancy losses into the net operating income to avoid artificially inflating the property value.
Capitalization Rate (Cap Rate):
This is the rate of return you would expect to earn on your investment. It is determined by dividing the net operating income by the property value. For example, if a property has a net operating income of $100,000 and is valued at $800,000, it would have a cap rate of 12.50%.
This, however, doesn’t factor in any financing so it only represents the return on investment if you were to purchase the property in cash. Financing can greatly alter your returns.
The capitalization rate is typically defined by the market. It is affected by the location and quality of an investment property as well as the access to amenities as well as investment risk.
Cap rate is expressed as a percentage with lower cap rates representing high quality, lower-risk investments. Don’t be fooled — just because a property has a high cap rate does not mean it is a good investment.
Income Approach Formula
The formula to calculate property value using the income capitalization approach formula is quite simple; the property value is equal to the net operating income divided by the cap rate.
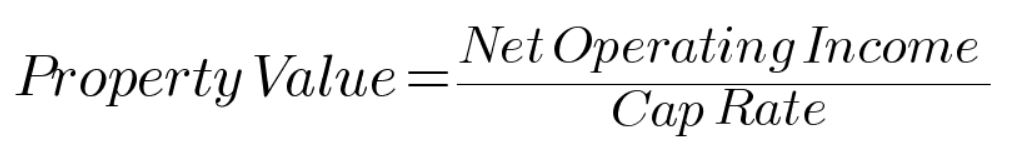
With this formula, we can see that the factors that increase the value of a property are either increasing net operating income (through increasing rent collected or decreasing expenses), or a lower cap rate.
Income Approach Example
Let’s take a look at an example of calculating a property’s value using the income approach.
For this example, let’s assume we’re considering a 20-unit apartment building with an average rent of $1200 per month. Multiplying 20 by $1200 yields a gross income of $24,000 per month or $288,000 per year.
Let’s also assume the property has $150,000 in annual operating expenses including vacancy loss. Deducting estimated operating expenses from the gross income leaves us with a net operating income of $138,000 per year.
In this example, the capitalization rate of the property based on its location, quality, and condition is 5%. If we divide the net operating income by the cap rate, we’ll get a value of $138,000 / 0.05 = $2,760,000.
Using The Income Approach To Determine Future Value Of A Property
The income approach can also be used to estimate the future value. Real estate investors can use this estimation to help determine the return on investment of a prospective property before making any investment decisions. Estimating the future value can help investors understand when they can take money out of the investment through a sale or refinance.
There are 2 basic methods for projecting the future value of a property. The first is the direct capitalization method (which is the method we used in the example above). The second is using the discounted cash flow which includes the time value of money.
Both methods look at the future cash flows of the property to determine its potential value in the future.
Direct Capitalization Method
The direct capitalization method is the simplest way to calculate future value. It uses the same income approach formula but uses an estimate of future cash flows instead of the current cash flow.
Let’s use the previous example to determine the value of the 20-unit apartment building 5 years in the future.
We’ll assume a conservative rent growth of 5% per year. Expenses will also increase at 5% per year.
In the fifth year, the property will charge an average rent of $1,460 per month and have a gross income of $350,400 per year. The annual expenses will be $182,325. The difference between the income and expenses yields a net operating income of $168,075.
Assuming the same capitalization rate of 5%, this property will have a value of $3,361,500 in year five. That’s an increase of just over $600,000 from the original value.
Discounted Cash Flow Analysis (DCF)
The DCF is a bit harder to calculate than the direct capitalization method, but it provides a more accurate representation of the future value. This is because it factors in the time value of money which states that money is more valuable today than it will be in the future.
This method determines the net present value of all future cash flows using a discount rate. A real estate professional can compare various investments using this method by choosing a desired rate of return. Running the DCF analysis for each property will show an investor the present value of the future cash flows in terms of today’s money.
The DCF formula does this by discounting future income generated from your property. So cash flow in the first year is more valuable than cash flow in future years.
Important Considerations For Using The Income Approach
While the income approach is a powerful tool for determining the market value of a property, there are a few things you should keep in mind. This approach to real estate valuation is useful in certain scenarios and with some caveats that can cause the formula to vary.
Income Producing Properties
The first caveat is the income capitalization approach is useful only for evaluating an income-producing property. This is true because the formula uses the net income from operations to determine the value. If a property hasn’t been built yet or has a high vacancy rate, the income method doesn’t work. Because of this, the direct capitalization method of the income approach should be used only on stabilized commercial real estate.
It is, however, possible to use this as a guideline to estimate the future value of income-producing real estate even if it is not yet producing profits.
Cap Rate Variation
The cap rate of a deal isn’t set in stone. There are a number of factors that can influence cap rate from geographic location, neighborhood, condition of the property, access to amenities, and many more. The cap rate is set primarily by the market but can vary on an individual deal.
Variations In Income And Expenses
Your rental income and operating costs will change over time. If you’re purchasing a real estate investment, you’re likely looking at the trailing-12 from the previous owner. You might, however, find that the net income the property generates changes when you take ownership of the property.
Repairs And Improvements
The income approach looks only at the operating income of the property. It does not consider any capital expenses which will affect your rate of return. It’s important for real estate investors to consider these large expenses when evaluating properties to ensure the return on investment matches your expectations.
Income Approach Compared To Other Methods
This article has detailed the income approach method for property valuation. But how does it compare to other methods? When should real estate investors use one of the various valuation methods?
Let’s dig into the primary three methods for determining the value of real estate investments.
Income Capitalization Approach
As we have seen in the income approach examples, this method uses the net operating income to determine the value of real estate investments. Therefore, it is useful for appraising stabilized, income-producing properties. This method works very well for commercial real estate like apartment complexes but does not work very well for single-family rental properties where the market value dictates the valuation.
Cost Approach
The cost approach is a real estate valuation method that estimates the value of income-producing real estate investments by looking at the replacement costs. This method is useful for new construction where there isn’t any income being generated yet.
Investors, however, can look at the potential gross income and expenses to get a sense of how much money they can make from a future sale.
Sales Comparison Approach
The sales comparison approach is the most common method for appraising single-family properties but can also be used in commercial real estate. It’s also known as the sales comparison method or market approach and uses recent, comparable sales of similar properties to estimate the value of a subject property.
Summary
The income approach is the primary tool used to determine the value of commercial real estate. This method takes into account all potential sources of income for a property, such as rent and other lease payments, parking fees, and so on. By understanding how this approach works, you can get a better idea of what your property is worth.
What other methods have you used to appraise income-producing real estate? Let us know in the comments below.

